In this tutorial you learn what it is SELinux and how to solve the error "Failed to load SELinux Policy" that appears on operating systems CentOS.
First, let's give a brief description of the security mode SELinux. What is it SELinux and what role it plays on the operating system Linux?
SELinux is a kernel security module, which has the role of controlling the access of software applications and users to the operating system. Released sometime around mid-2000, SELinux has become over the years present on more and more distributions of Linux.
The activity of this module consists in the distribution and control of security policies in the system, limiting the access of applications at the level of major subsystems of the kernel.
This security mechanism works independently of the traditional control and blocking systems of suspicious activities, present on Linux. Cannot be actively controlled by superuser "root” and without interaction with third-party applications or scripts, SELinux provides core stability.
Security of a system Linux without this module SELinux it will automatically depend on the correctness of the kernel configuration, applications with running privileges and their configurations. A simple error in one of these previously mentioned elements can compromise the correct functioning of the entire system.
In conclusion, SELinux can be called a real guardian of operating systems Linux, ensuring integrity, security and stability. Do not confuse this module with an antivirus or a firewall. It's totally different.
Users running Linux for web and cloud servers I know well that SELinux may cause problems in running software applications with system access and control level privileges.
SELinux can control operating system activities for each user, application and daemon in part and may apply precise security policies and restrictions. This can often be a problem for web servers, where most specific software processes have privileges and interact with the operating system kernel.
Those who decided to disable this kernel module often make mistakes in modifying the directives, which leads to the inability to load SELinux when restarting the operating system. “Failed to load SELinux policy".
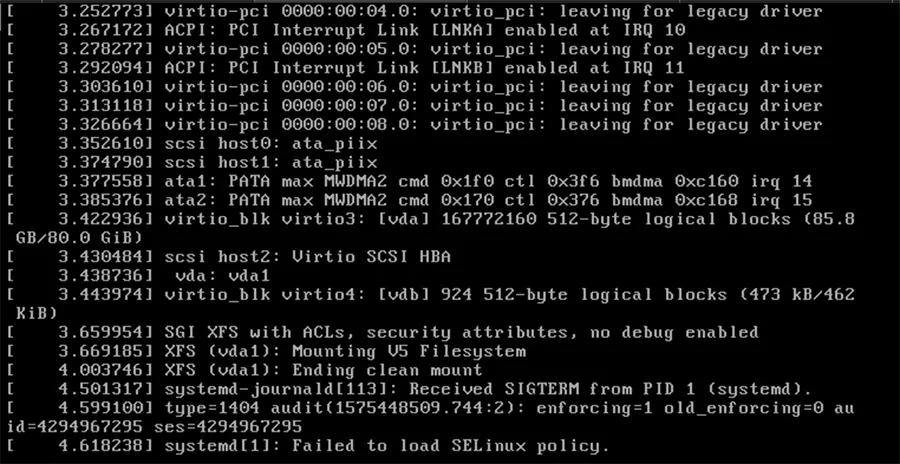
I showed in a article how it can be disabled SELinux, to prevent interrupting the process put by the NGINX service in a web server.
# This file controls the state of SELinux on the system.
# SELINUX= can take one of these three values:
# enforcing - SELinux security policy is enforced.
# permissive - SELinux prints warnings instead of enforcing.
# disabled - No SELinux policy is loaded.
SELINUX=permissive
# SELINUXTYPE= can take one of three two values:
# targeted - Targeted processes are protected,
# minimum - Modification of targeted policy. Only selected processes are protected.
# mls - Multi Level Security protection.
SELINUXTYPE=disabled (WRONG)An error that we inadvertently made, and since it was a remote server, the solution was complete reinstallation of the operating system.
If you are a bit luckier, you can correct SELinux only if you have a DVD at hand or the ability to load the ISO image of the operating system in "rescue".
Failed to load SELinux Policy it is found especially on the versions CentOS 6, CentOS 7, RHEL 7.x.
Thanks for the article, you get the root cause but missed one solution: actually add selinux=0 in the OS entry proposed by grub is enough to disable selinux and made the OS bootable again.
Thanks for this solution!
selinux=0I think that at the time I wrote the article, this option was not available. I may be mistaken. Thanks for the solution!